
Zero Trust Architecture is becoming essential for cloud web security as organizations face increasing threats. By adopting a zero trust model, businesses can enhance their data protection and ensure that every user and device is continuously verified. Insights for 2025 suggest that this approach will be crucial in mitigating risks associated with remote work and evolving cyber threats, shaping the future of cybersecurity strategies.
As organizations increasingly migrate to cloud environments, the need for robust security measures has never been more critical. One of the most effective frameworks gaining traction is **Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)**. This article delves into the role of Zero Trust Architecture in enhancing **cloud web security**, offering insights for 2025 and beyond.
Zero Trust Architecture is predicated on the premise that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter. This model operates under the mantra of "never trust, always verify." By implementing ZTA, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber threats in their cloud environments.
The core components of Zero Trust include:
As businesses transition to cloud-based services, the attack surface expands, making **cloud web security** a paramount concern. Traditional security measures often fail to address the complexities and vulnerabilities inherent in cloud environments. Here, ZTA plays a transformative role.
By adopting Zero Trust principles, organizations can enhance their cloud web security posture. This approach not only mitigates risks but also ensures compliance with various regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR and HIPAA, which mandate stringent data protection measures.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture involves several strategic steps:
Looking ahead to 2025, several trends are expected to shape the landscape of Zero Trust Architecture and cloud web security:
While the benefits of Zero Trust Architecture are clear, organizations may face several challenges during implementation:
As we move toward 2025, the role of Zero Trust Architecture in cloud web security will become increasingly vital. Organizations that embrace ZTA will be better positioned to combat evolving cyber threats and protect sensitive data. By prioritizing user identity verification, device compliance, and continuous monitoring, businesses can create a resilient security environment that not only enhances their cloud web security but also fosters trust among users and stakeholders.
In conclusion, the strategic implementation of Zero Trust Architecture is no longer optional; it is a necessary evolution in the face of rising cybersecurity challenges. With the right approach and commitment to ongoing improvement, organizations can secure their cloud environments against the threats of tomorrow.

Top Cloud Web Security Solutions in 2025: Protect Your Business in the Cloud

The Future of Cloud Web Security in the USA: Trends to Watch in 2025
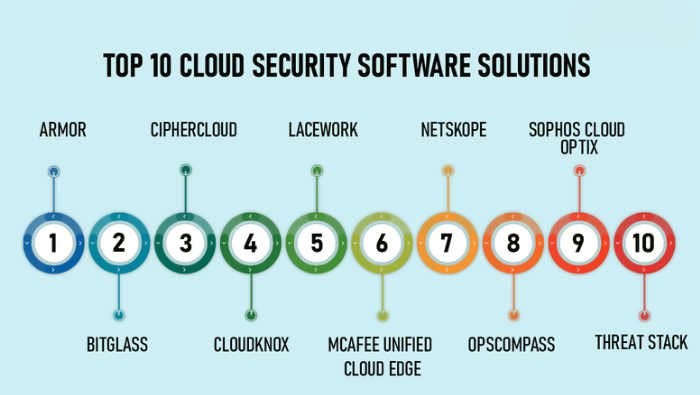
Top Cloud Web Security Solutions for Businesses in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
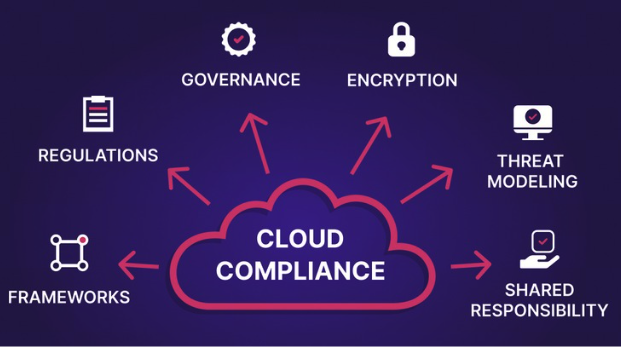
Navigating Compliance: Cloud Web Security Regulations in the USA by 2025
How AI is Shaping Cloud Web Security Strategies in the USA for 2025

Cloud Web Security Best Practices for Small Businesses in the USA: 2025 Edition

The Impact of Remote Work on Cloud Web Security: 2025 Trends and Solutions

The Role of Technology in Personal Injury Law: Insights for 2025